Neurohacking Experiments - EEG Reading Profile Report Analysis
Here is a comparison of the results from the two EEG readings I did before and after the 3 month Neurohacking Experiments:
Pathology - 20% increase in Delta Power
Arousal - 10% decrease in Low Delta Power
Arousal can be described as the activation of the autonomous nervous system (ANS) and the central nervous system (CNS). It is related to mental alertness and is reflected by heart rate, heart rate variability, pupil dilation and muscle tone. Arousal level is very important for mental performance.
Default Mode Network:
Network Activity - 30% decrease in Hyper-Active & 30% decrease in Hypo-Active
Network Connectivity - 27% decrease in Hyper-Connected & 7% decrease in Hypo-Connected
The DMN is active during rest and is associated with self-reflective processes or mental stimulation. The DMN consists of frontal brain areas that are known to be involved in higher executive functions such as working memory, planning and cognitive control.
Dorsal Attention Network:
Network Activity - 50% decrease in Hyper-Active & 34% decrease in Hypo-Active
Network Connectivity - 14% decrease in Hyper-Connected & 13% decrease in Hypo-Connected
The DAN consist of front and parietal areas which are important for higher executive functions, such as working memory, goal-directed actions and attention. The DAN consists of the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex (DLPFC), which is associated with cognitive control, working memory and awareness. The Inferior Parietal Lobule, which is important for goal-directed action, creativity and reasoning and the Superior Parietal Lobule, which is known to be involved in imagination, advanced motor skills and visual attention.
The Emotion- Regulation Cortex:
Network Activity - 37% decrease Hyper-Active
Network Connectivity - 10% decrease Hyper-Connected 4% increase Hypo-Connected
The ERC plays a role in emotion regulation, empathy, risk assessment, decision making and fear processing. The ERC consists of the Middle Frontal Gyrus, which is involved in emotional decision making and the Orbitofrontal Gyrus, which is known for it’s role in the evaluation of emotional stimuli and the representation of the somewhat intangenable concepts of personality or ‘cognitive style’.
The Sensory-Motor Complex:
Network Activity - 62% decrease Hyper-Active & 75% decrease Hypo-Active
Network Connectivity - 9% decrease Hyper-Connected & 7% increase Hypo-Connected
The SMC is responsible for somatosensory processing (the sense of touch) and preparing and executing motor actions. The Primary Somatosensory and Motor Cortices are involved in the sense of touch and executing actions, respectively. The Secondary Somatosensory Cortex is involved with higher level of somatosensory processing such as the integration of proprioceptive information with visual information to create a sense of the body in space. The Premotor cortex is resonpsible for preparing actions and also contains visumotor neurons that respond to viewing the actions of others. This system is called the ‘mirror neuron system’
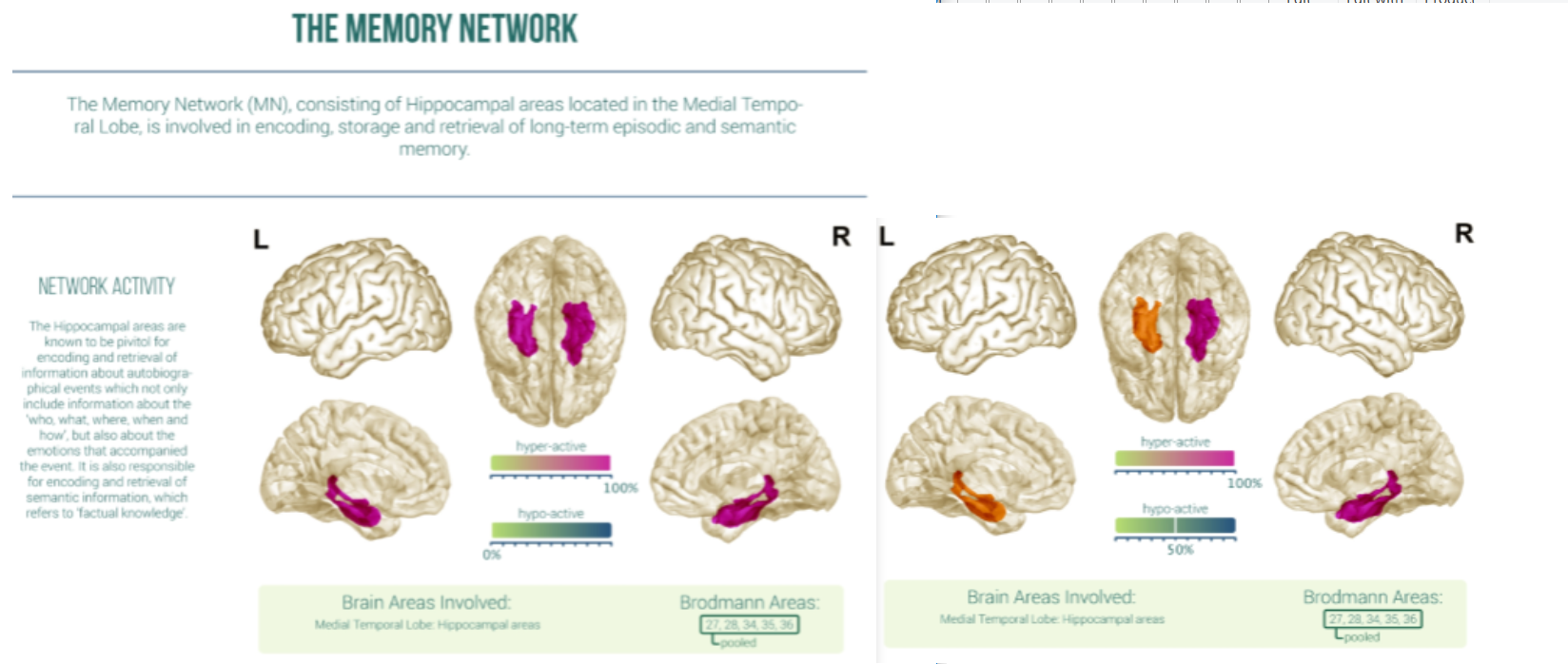
The Memory Network:
Network Activity - 50% increase Hypo-Active
Network Connectivity - 5% decrease Hyper-Connected & 11% decrease Hypo-Connected
The MN consisting of Hippocampal areas located in the Medial Temporal Lobe is involved in encoding storage and retrieval of long-term episodic and semantic memory. The Hippocampal areas are known to be pivitol for encoding and retrieval of information about autobiographical events which not only include informaiton about the ‘who, what, where, when and how’, but also about the emotions that accompanied the event. It is also responsible for encoding and retrieval of semantic information which refers to ‘factual knowledge’
The Visual Cortex
Network Activity - 17% decrease Hypo-Active
Network Connectivity - 7% increase Hyper-Connected & 27% increase Hypo-Connected
The VC is a group of occipital brain areas that is specialized in processing visual information. The VS is hierarchically organized with respect to the complexity of visual features that it processes. Low-level visual features, such as color, contrast levels and line orientations are processed in the primary visual cortex.
This is just a breakdown of the results and the percentage changes that occurred pre & post the Neurohacking Experiments.
A key concept to consider is that with neurohacking and attempting to improve your cognitive function, during the period of growth you may actually see a reduction/decrease/lull in some areas as conditions are improving. I like to think of it similar to a muscle group where following training there is soreness and pain during the recovery process that may seem to hinder or reduce your mobility/movement. Just because there are wild improvements or wild retrogression in certain areas it doesn’t mean these will sustain long term. Of course further testing would need to be done to get more conclusive information (I would like to see another EEG reading done 3 months after no Neurohacking and even every 3 months following) but in general I believe this displays that with Neurohacking and the factors I implemented during those 3 months (like meditation, nootropics, mindfullness, brain games, etc) quantifiable changes occur in the brain in many different areas as these results display after completing this EEG readings.